Frequently Asked Questions
How does one use the MXP I/O Expansion capability?
The “MXP I/O Expansion” example program demonstrates the use of the MXP I/O Expansion capabilities of the navX-MXP, including the following capabilities:
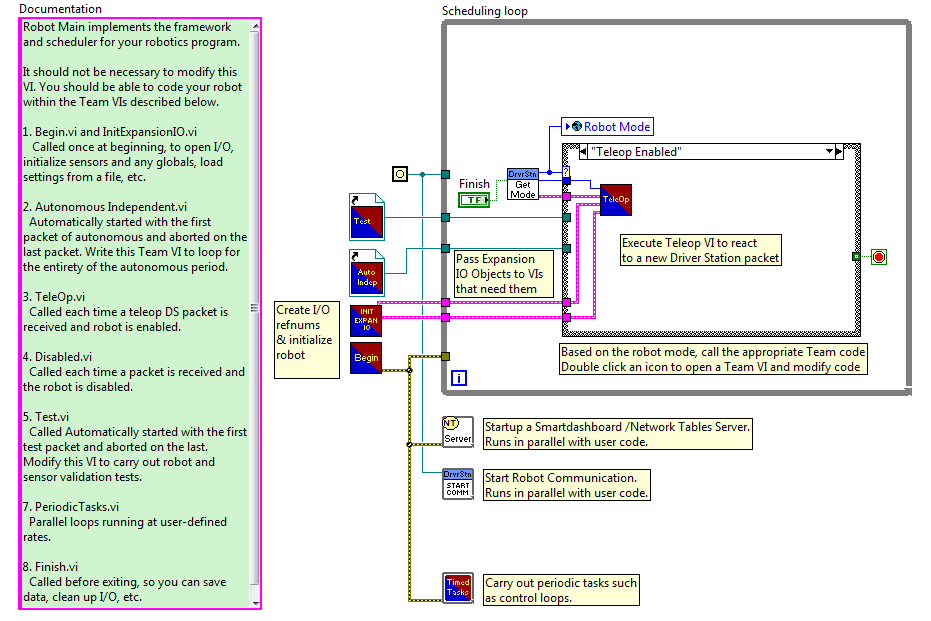
The RobotMain.vi invokes the InitExpansionIO.vi during initialization, and routes the resulting DigitalIoObjects and AnalogIoObjects clusters to the Teleop.vi.
Full LabVIEW Project on GitHub
DIGITAL I/O
- Pulse-Width Modulation [PWM] (e.g., Motor Control)
- Digital Inputs (e.g., Contact Switch closure)
- Digital Outputs (e.g., Relay control)
- Quadrature Encoders (e.g., Wheel Encoder)
ANALOG I/O
- Analog Inputs (e.g., Ultrasonic Sensor)
- Analog Input Trigger (e.g., Proximity Sensor trigger)
- Analog Trigger Counter
- Analog Output (e.g., Constant-current LED, Sound)
FRC C++ Example
Full C++ source code on GitHubFRC Java Example
Full Java Source code on GitHubFRC LabView Example
The navX-MXP FieldCentric-Drive LabView example shows how to make small modifications to the LabView “FRC RoboRIO Robot Project” using the “Mecanum Robot” configuration to implement high-accuracy Field-Centric drive.RobotMain.vi

The RobotMain.vi invokes the InitExpansionIO.vi during initialization, and routes the resulting DigitalIoObjects and AnalogIoObjects clusters to the Teleop.vi.
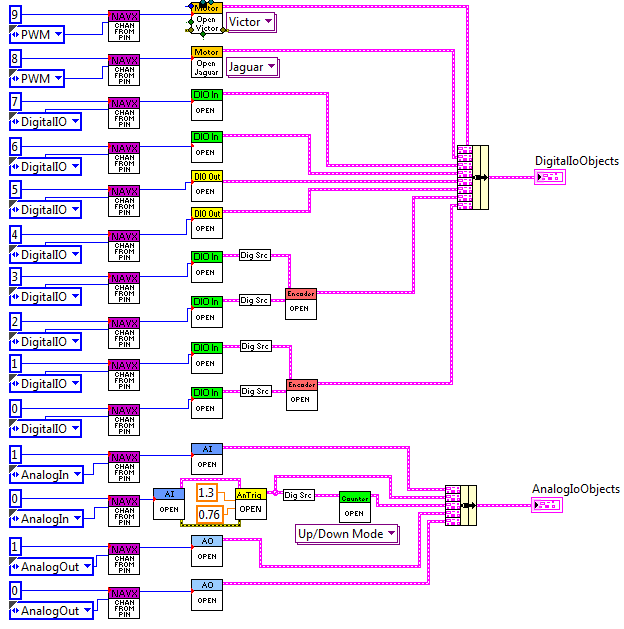
InitExpansionIO.vi
The InitExpansionIO.vi instantiates the various objects which map onto the navX-MXP Expansion IO Pins.
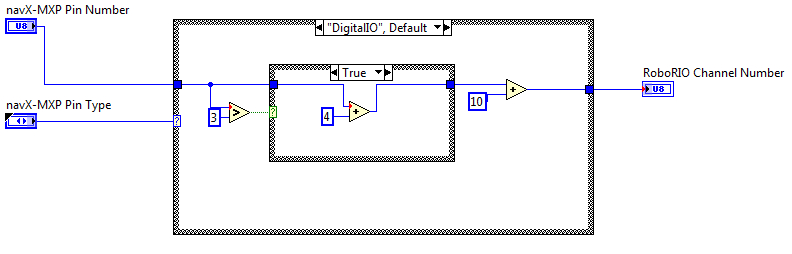
GetChannelFromNavX-MXPPin.vi
The GetChannelFromNavX-MXPPin.vi performs the translation from the navX-MXP Digital or Analog Pin number to the corresponding RoboRIO Channel Number, which is provided to the various VIs that open that particular port.
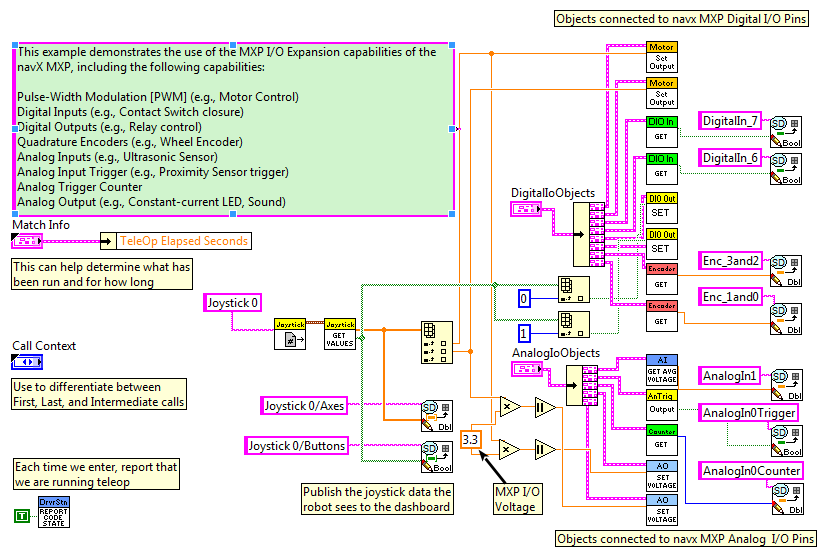
Teleop.vi
The Teleop.vi reads the Joystick inputs and programs the output pins accordingly (PWM to motor controllers, Digital Outputs and Analog Outputs). As well, values from the input pins (Digital Inputs, Encoders and Analog Inputs) is retrieved and displayed on the Smart Dashboard.
Full LabVIEW Project on GitHub
Last Updated 8 years ago