Frequently Asked Questions
What is field-oriented drive, and how does one implement it?
Field-Oriented Drive (FRC)
 An easy-to-use, highly-maneuverable drive system is at the heart of a successful FIRST Robotics Challenge (FRC) robot. Omnidirectional drive systems provide motion in the Y axis (forward-backward), X-axis (strafe), and Z axis (rotating about it’s center axis). Each “degree of freedom” is independent, meaning that the overall robot motion is comprised of a “mix” of motion in each of the X, Y and Z axes, control of which is easily provided with a 3-degree of freedom joystick. This resulting maneuverability is quite useful during FRC competitions to avoid other robots, pick up and place game pieces, line up for shooting to a target, etc. Yet the driver who remains in a fixed position is now presented a new challenge: when the driving joystick is pushed forward, the robot does not necessarily move forward with respect to the field – rather it moves forward with respect to the robot. This forces the driver to develop the skill of “placing their head in the robot” and performing the angular transformation mentally. This skill can take quite awhile to develop meaning that rookie drivers face an uphill climb before they can be productive team contributors. Additionally, the mental energy involved in field-to-robot rotational transformations reduces the driver’s cognitive ability to focus other game-related tactical tasks, as evidenced by drivers who are so intently focused on driving that their response to their teammates is diminished. Moreover, when the driver does not have a clear line of sight to the robot, the “head in the robot” becomes even more challenging.
An easy-to-use, highly-maneuverable drive system is at the heart of a successful FIRST Robotics Challenge (FRC) robot. Omnidirectional drive systems provide motion in the Y axis (forward-backward), X-axis (strafe), and Z axis (rotating about it’s center axis). Each “degree of freedom” is independent, meaning that the overall robot motion is comprised of a “mix” of motion in each of the X, Y and Z axes, control of which is easily provided with a 3-degree of freedom joystick. This resulting maneuverability is quite useful during FRC competitions to avoid other robots, pick up and place game pieces, line up for shooting to a target, etc. Yet the driver who remains in a fixed position is now presented a new challenge: when the driving joystick is pushed forward, the robot does not necessarily move forward with respect to the field – rather it moves forward with respect to the robot. This forces the driver to develop the skill of “placing their head in the robot” and performing the angular transformation mentally. This skill can take quite awhile to develop meaning that rookie drivers face an uphill climb before they can be productive team contributors. Additionally, the mental energy involved in field-to-robot rotational transformations reduces the driver’s cognitive ability to focus other game-related tactical tasks, as evidenced by drivers who are so intently focused on driving that their response to their teammates is diminished. Moreover, when the driver does not have a clear line of sight to the robot, the “head in the robot” becomes even more challenging.Solving this challenge is conceptually straightforward. First, the current angle (θ) of rotation between the head of the field, and the head of the robot must be measured; secondly, the joystick X/Y coordinates are transformed by θ, as shown in following pseudo-code:
The WPI Library “MecanumDrive_Cartesian()” function and the LabView “Holonomic Drive” VI, which are used in the examples below, implement the field-centric drive algorithm. The navX-MXP “Yaw” angle is provided to these library functions to specify the amount of rotation between the robot and the field.double rcw = pJoystick->GetTwist(); double forwrd = pJoystick->GetY() * -1; /* Invert stick Y axis */ double strafe = pJoystick->GetX(); float pi = 3.1415926; /* Adjust Joystick X/Y inputs by navX MXP yaw angle */ double gyro_degrees = ahrs->GetYaw(); float gyro_radians = gyro_degrees * pi/180; float temp = forwrd * cos(gyro_radians) + strafe * sin(gyro_radians); strafe = -forwrd * sin(gyro_radians) + strafe * cos(gyro_radians); fwd = temp; /* At this point, Joystick X/Y (strafe/forwrd) vectors have been */ /* rotated by the gyro angle, and can be sent to drive system */
For more details on field-centric drive algorithms, please see this excellent post on Chief Delphi by Ether which provides a wealth of helpful, well written information on implementing field-centric drive on various types of drive systems.
FRC C++ Example
Full C++ source code on GitHubFRC Java Example
Full Java Source code on GitHubFRC LabView Example
The navX-MXP FieldCentric-Drive LabView example shows how to make small modifications to the LabView “FRC RoboRIO Robot Project” using the “Mecanum Robot” configuration to implement high-accuracy Field-Centric drive.RobotMain.vi
Place the NavX main vi on the block diagram and set it up to your needs. The default sample rate is 50Hz. You may need to process faster for your situation. For the SPI, I2C and USB connections the max sample rate is 200Hz.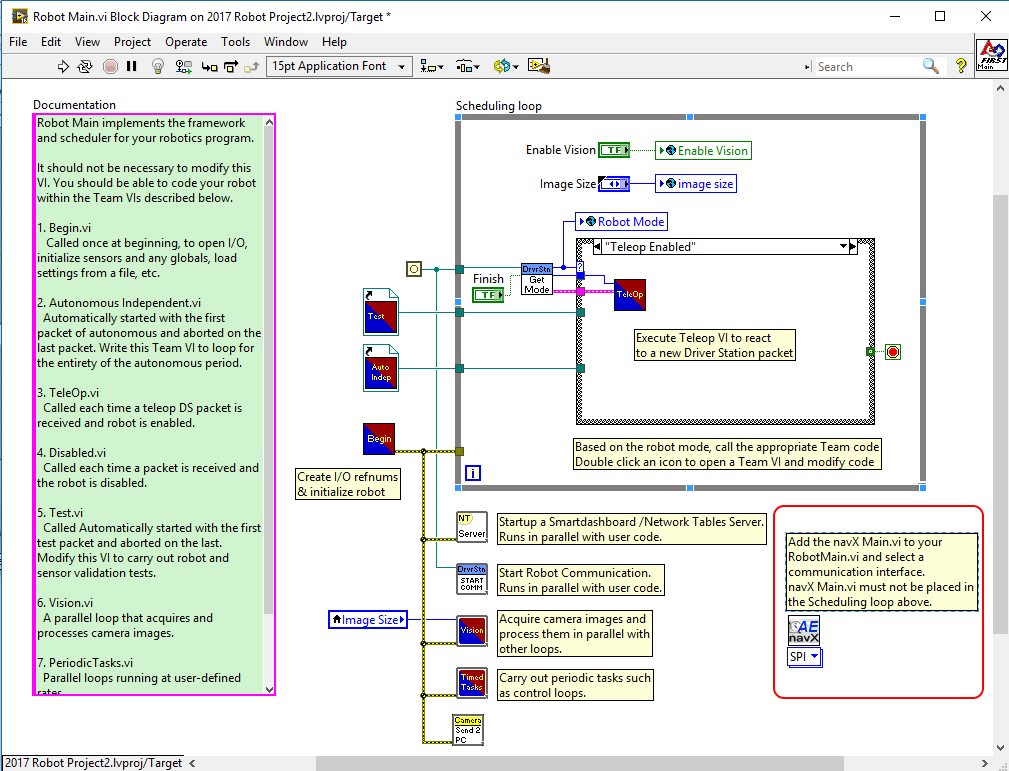
Teleop.vi
The Teleop.vi is modified to feed the current navX-MXP “Yaw” angle reading to the Holonomic Drive VI, which rotates the joystick X/Y coordinates by the gyro angle (and thus implements FieldCentric drive control). Additionally, if a driver joystick button is pressed, the navX-MXP “Yaw” angle is reset to zero. The navX-MXP Device TypeDef is passed to the Teleop.vi via a VI input terminal.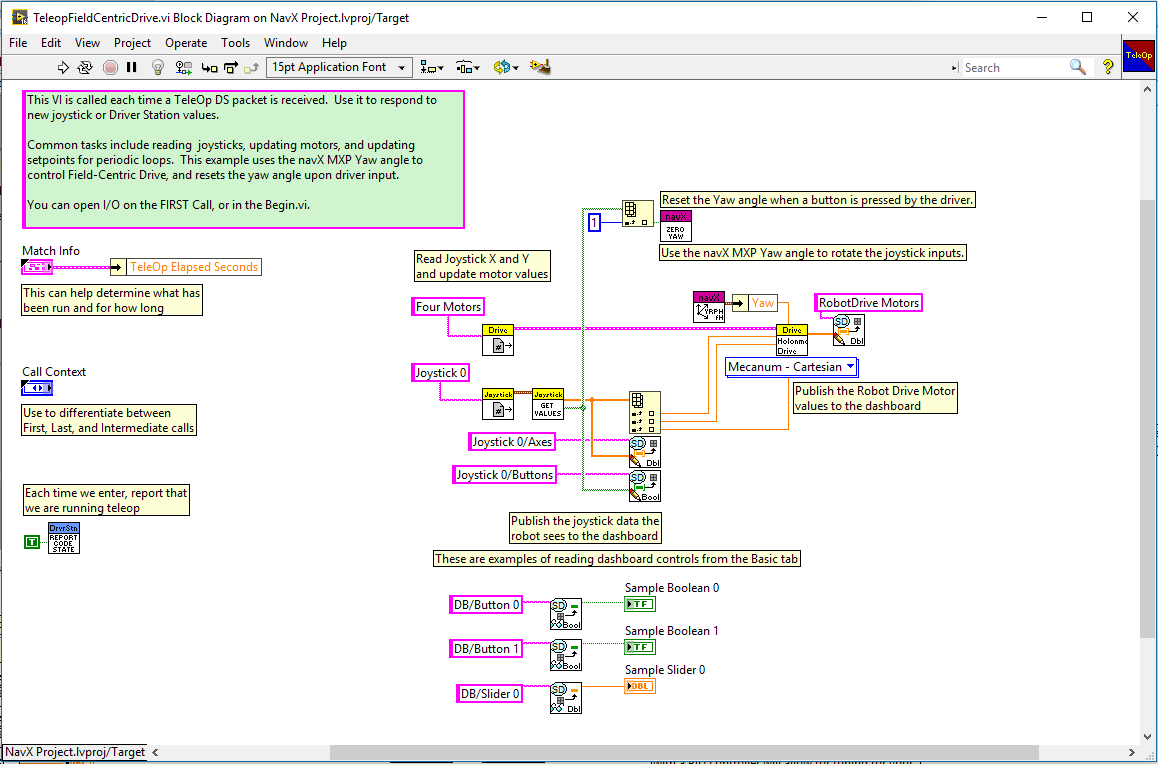
Full LabVIEW Source code on Github
Last Updated 9 years ago